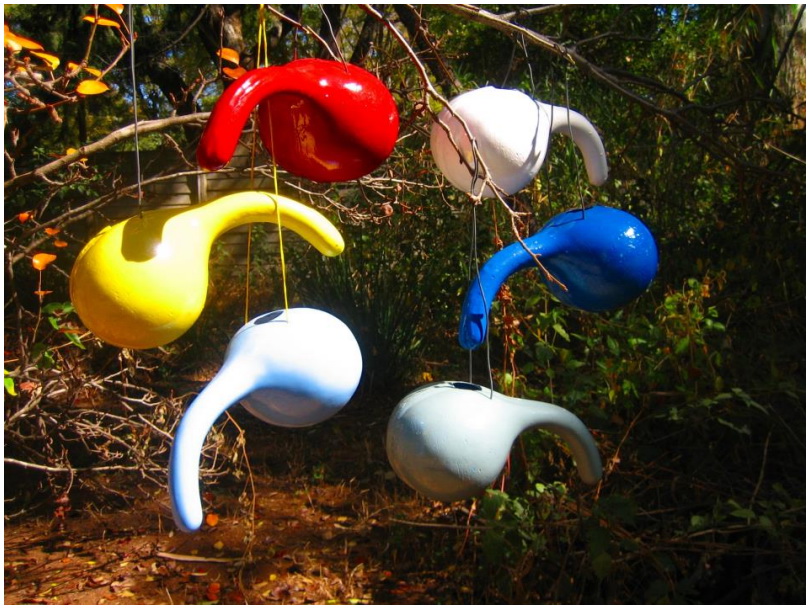
Dr. Peter Morgan, winner of the 2013 Stockholm Water Prize and resident of Zimbabwe, recently shared the design of The Mukombe on the forum of the Sustainable Sanitation Alliance. The Mukombe is a hand washing device – a “tippy tap” as it is commonly known within the Water, Sanitation & Hygiene (WASH) scene – as it just requires a little tip to provide the user with just enough water to wash the hands. In water-arid areas, such a simple device can be essential to hygiene.
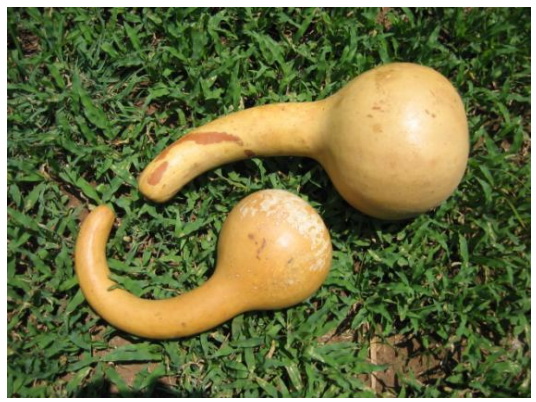

“(The Mukombe) was first conceived by Dr Jim Watt when he worked in Zimbabwe as a Salvation Army doctor in Chiweshe in the late 1970′s. (…) This vegetable had a hard shell and could be used as a gourd or calabash for carrying water and other commodities. It is commonly grown in the fields. The great innovation was to turn this common plant into a hand washing device. (…) Many years ago I made a fibre glass replica of this remarkably simple and elegant device. Many if not most natural plants did not have the right shape. Using the fibre glass replica with its idealised shape, Prodorite in Harare have been able to mass produce the product. The mukombe holds about 2 litres of water and can provide enough water in a single filling to give about 35 hand washes.”
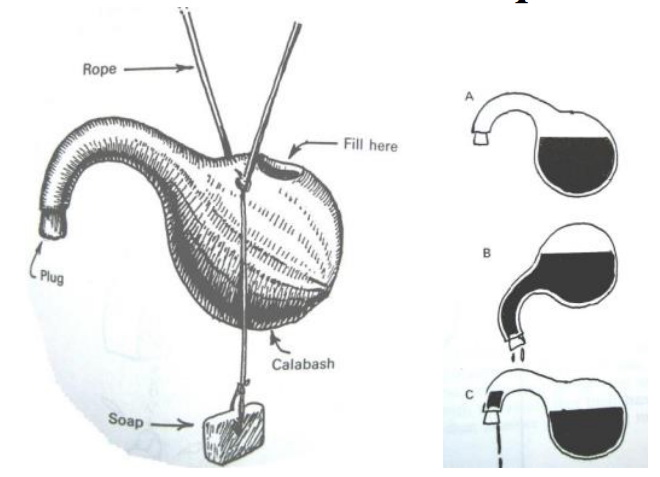
“Modifications are made to the naturally occurring Mukombe. An opening is made in the top and a cork or plug is placed at the end of the neck as shown above, with a small opening for water to drain. Holes are drilled into the top of the mukombe and a string passed through. The mukombe is suspended by the string so that it lies at a special angle. The mukombe is filled with water and then tipped up so that some water passes up the neck. When the mukombe comes to its resting position again, some water is left at the end of the neck and slowly drains out. It is this water which is used to wash the hands. The flow stops automatically when the small reservoir in the neck runs out.” (source)
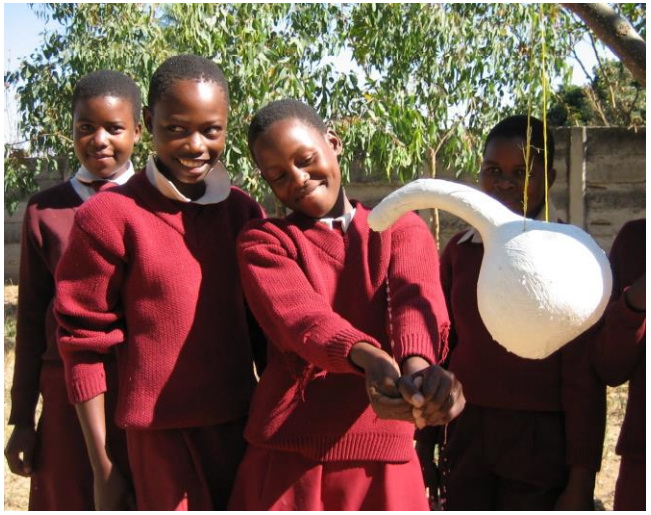

The beauty of the Makombe over other tippy taps is that the design is based on a naturally grown product and that it only uses a very little amount of water. Plus: you can hang it anywhere, there is no need for an advanced construction. Clearly another winner in the “it’s cheap, it works, it wins”-category.
Avid readers may remember Dr. Morgan as the inventor of the Blair Ventilated Improved Pit (VIP) Latrine, which has meanwhile been adapted as the national standard by the government of Zimbabe.